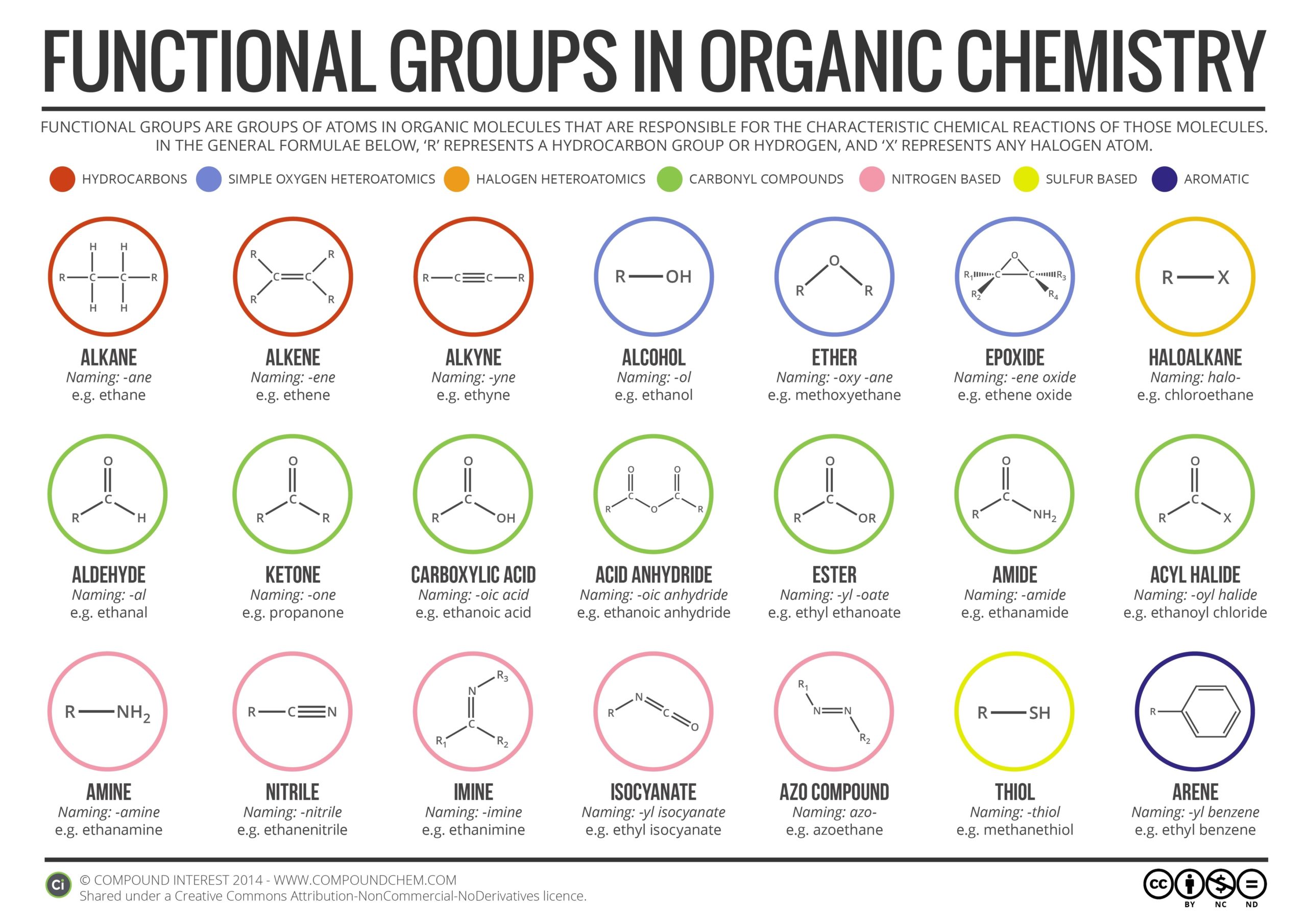
Functional groups are structural units within organic compounds that are defined by specific bonding arrangements between specific atoms. They are the key structural elements that define how organic molecules react. In this response, I will provide an overview of the most common functional groups in organic chemistry.
Alkanes are organic compounds that contain only single bonds between carbon atoms and hydrogen atoms. They are also known as saturated hydrocarbons. Alkanes are the simplest organic compounds and are characterized by their relatively low reactivity. Methane, CH4, is the simplest alkane example, and is the natural gas you may burn in your furnace. Octane, C8H18, is a component of gasoline.
Alkenes are organic compounds that contain at least one carbon-carbon double bond. They are also known as olefins. Alkenes are more reactive than alkanes due to the presence of the double bond. Ethene, the simplest alkene example, is a gas that serves as a cellular signal in fruits to stimulate ripening. Ethyne, commonly called acetylene, is used as a fuel in welding blow torches.
Alkynes are organic compounds that contain at least one carbon-carbon triple bond. They are less common than alkenes and alkanes. Alkynes are more reactive than alkenes due to the presence of the triple bond. The simplest alkyne example is ethyne, commonly called acetylene, which is used as a fuel in welding blow torches.
Alkyl halides are organic compounds that contain a halogen atom (fluorine, chlorine, bromine, or iodine) bonded to a carbon atom. They are also known as haloalkanes. Alkyl halides are more reactive than alkanes due to the presence of the halogen atom. They are used in a variety of applications, including refrigeration, air conditioning, and as solvents.
Alcohols are organic compounds that contain a hydroxyl (-OH) group bonded to a carbon atom. They are characterized by their ability to form hydrogen bonds with water molecules. Alcohols are used in a variety

