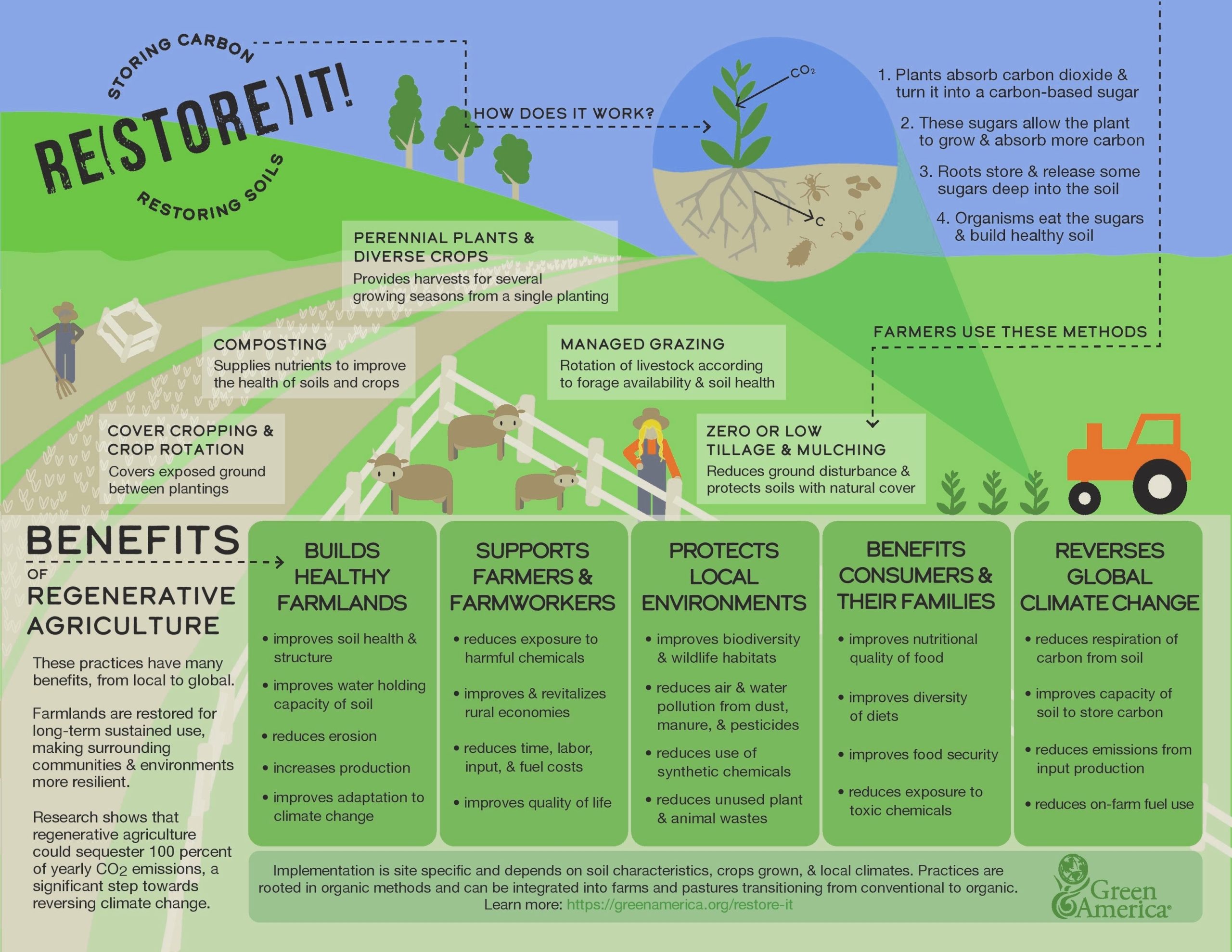
Regenerative Agriculture is a farming practice that focuses on improving soil health by enhancing the functioning of the systems on which it relies. It is a way of farming that aims to restore soil health, increase biodiversity, and improve the resilience of ecosystems. Regenerative Agriculture is based on the principles of agroecology, which emphasizes the importance of ecological processes in agriculture. It is a holistic approach to farming that takes into account the entire ecosystem, including the soil, water, air, and living organisms.
Regenerative Agriculture is a response to the negative impacts of industrial agriculture, which has led to soil degradation, loss of biodiversity, and environmental pollution. Industrial agriculture relies heavily on chemical fertilizers, pesticides, and herbicides, which have negative impacts on soil health and the environment. Regenerative Agriculture, on the other hand, focuses on natural processes to improve soil health and increase productivity.
One of the key principles of Regenerative Agriculture is soil health. Healthy soil is essential for plant growth and productivity. Regenerative Agriculture practices focus on improving soil health by increasing soil organic matter, reducing soil erosion, and improving soil structure. This is achieved through practices such as cover cropping, crop rotation, and reduced tillage.
Another important principle of Regenerative Agriculture is biodiversity. Biodiversity is essential for ecosystem health and resilience. Regenerative Agriculture practices aim to increase biodiversity by promoting the growth of native plants, reducing the use of pesticides and herbicides, and providing habitat for wildlife.
Regenerative Agriculture also emphasizes the importance of water management. Water is a precious resource, and Regenerative Agriculture practices aim to conserve water and improve water quality. This is achieved through practices such as rainwater harvesting, irrigation management, and the use of cover crops to reduce evaporation.
Regenerative Agriculture has many benefits, including increased soil health, increased biodiversity, and improved water quality. It also has the potential to increase productivity and profitability for farmers. Regenerative Agriculture practices can reduce the need for chemical inputs, which can save farmers money and reduce their environmental impact.
In conclusion, Regenerative Agriculture is a holistic approach to farming that focuses on improving soil health

