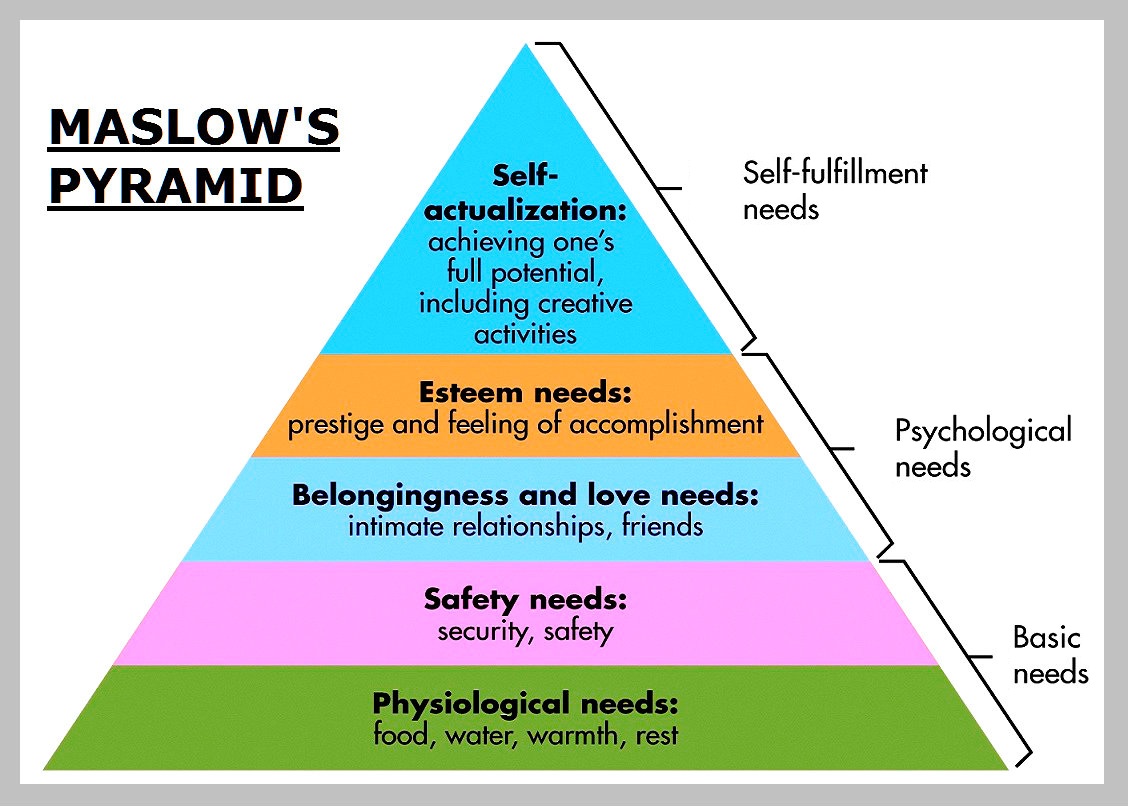
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs (also known as Maslow Pyramid) is a psychology framework developed by Maslow to explain various human needs and basis for motivation. The pyramid is one of the founding blocks of the theory of human motivation widely used in psychology and business. It divides all human needs into 3 buckets: basic needs, psychological needs and self-fulfillment needs.
The basic needs include physiological (food, water, warmth and rest) and safety, sense of security and protection. These are the founding blocks that are a must before more high level needs can be achieved. Moving up the pyramid, one must achieve a sense of belongingness and love, which comes with intimate relationships and friendships. Esteem needs come next. These come from prestige and feeling of accomplishment. At the top of the hierarchy is self-actualization, which is achieving one’s full potential including creative activities.
The key concept behind the pyramid is the fact that one can only move up, provided that the more basic needs are satisfied. For example, if an employee feels that their job is under a threat, Maslow’s theory suggests that this employee will be less productive, because they cannot realize higher level potential due to the safety concerns.
Tags: hierarchy of needs, maslow pyramid, maslow theory of human motivation, Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs, maslows hierarchy